Is your lower back pain making it difficult to enjoy everyday activities? It might be more than just a simple muscle strain. Sacroiliac (SI) joint dysfunction is a common but often overlooked cause of lower back pain, affecting millions of people worldwide. Fortunately, there are 3 tests to tell you if your back pain is caused by SI joint dysfunction. Below, we’ll go through the three most commonly used physical tests, as well as other tests that can be used to diagnose SI joint dysfunction.
If you’re experiencing chronic low back pain, you may be dealing with sacroiliac joint dysfunction. Luckily, we at the Advanced Spine Center can perform a variety of tests in order to properly diagnose you. Schedule an appointment with board-certified specialist Stephen P. Courtney, MD today and start your journey toward recovery.
Ready to schedule an appointment? Call (972) 499-5457 today!
What Is Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction occurs when there is an abnormality in the sacroiliac joint, which connects the pelvis to the lower spine. This dysfunction can lead to sacroiliac joint pain and discomfort, which can be felt in the lower back, buttocks, and sometimes even in the legs. It often manifests as a dull or sharp ache in the affected area, which may be worsened by activities such as standing, walking, or climbing stairs.
Common treatments for sacroiliac joint pain and dysfunction include medication therapy, physical therapy, SI joint steroid injections, and SI joint fusion.
How to Diagnose SI Joint Dysfunction
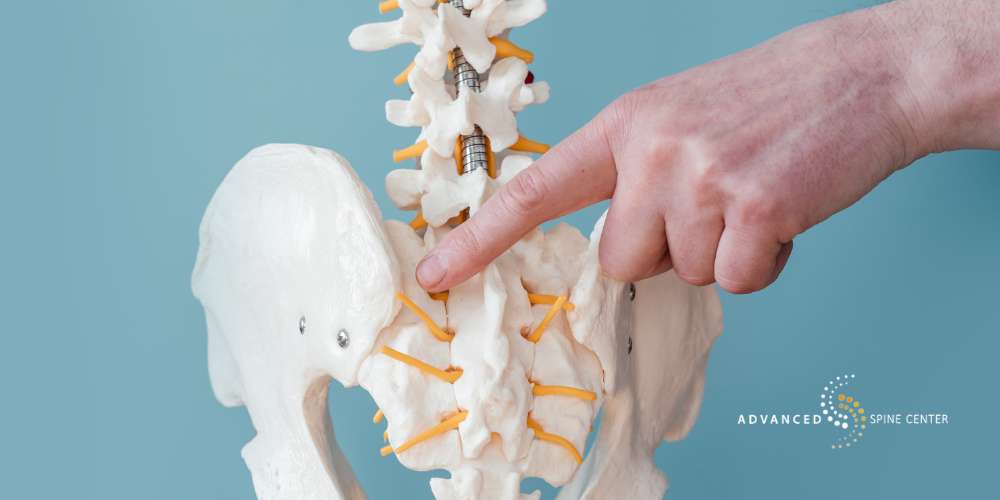
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction can be diagnosed through a physical examination, as well as a medical history assessment and various imaging tests. Since there are a number of different conditions that could manifest as lower back pain, examiners will perform multiple physical tests in order to ensure an accurate diagnosis of SI joint dysfunction.
If the examiner performs one physical test, and the patient experiences pain that mimics their normal SI pain, then that’s considered a positive test result. Three or more positive test results would indicate that the patient may have sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
What Are 3 Tests to Tell You If Your Back Pain Is Caused by SI?
There are a number of different ways that SI joint dysfunction can be diagnosed, but there are three primary physical exams physicians will use to diagnose issues with the body’s sacroiliac joints. These include the FABER test, thigh thrust test, and Gaenslen test.
Patrick FABER Test
One main test used to diagnose sacroiliac joint issues is Patrick’s test, or the FABER test. During the test, the patient lies on their back with one leg bent at the knee and their foot resting on the opposite knee, forming a figure-four shape.
The examiner then applies gentle pressure to the bent knee while stabilizing the opposite hip, moving the knee outwards. If the patient experiences pain in the sacroiliac joint or groin area, it may indicate dysfunction in the joint. This test can also be used to diagnose hip joint dysfunction.
Thigh Thrust Test
The thigh thrust test, or sheer test, is another physical exam used to identify sacroiliac joint dysfunction. In this test, the patient lies on their back with their unaffected leg straight, and the leg on the affected side bent at a 90-degree angle. The examiner then, while applying pressure to the opposite hip, applies pressure directly downward on the bent knee.
If the patient experiences pain in their sacroiliac joint, then they likely have sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
Gaenslen Test
The Gaenslen test can also be used to diagnose SI joint dysfunction. During the test, the patient lies on their back with their affected side on the edge of the examination table. One leg is brought toward the chest while the other leg hangs off the table, allowing the pelvis to tilt and stretch the sacroiliac joint.
The examiner then applies pressure to the extended leg, further stressing the joint. If the patient feels pain in their SI joint, it may indicate dysfunction in the joint.
Other SI Joint Tests

In addition to the above three tests, there are several other methods that examiners may use when diagnosing SI joint dysfunction. Below are some of these additional SI joint tests.
Yeoman Test
Yeoman’s test is performed with the patient lying prone (face down) on the examination table with one leg straight and one leg bent at the knee (with their foot facing the ceiling). The examiner then places pressure above the tailbone on the affected side.
The examiner holds the patient’s leg just above the knee and pulls upwards, hyperextending the hip and putting stress on the sacroiliac joint. If the patient is experiencing SI joint dysfunction, then they will likely experience pain during this test.
SI Distraction Test
Another test used to diagnose SI joint dysfunction is the SI distraction test. During the test, the patient lies supine on the examination table with both legs extended. Then, the examiner stands on one side of the patient, and simultaneously applies pressure to both sides of the patient’s pelvic bone. If this reproduces the patient’s SI joint pain, then they may have a sacroiliac joint issue.
Fortin Finger Test
The Fortin finger test can help examiners determine whether the patient is experiencing SI pain or pain as a result of another lower back issue. During the Fortin finger test, the examiner asks the patient to point to the exact spot where they are experiencing the most pain. The examiner notes where the patient has pointed to and asks the patient to relax.
5 to 10 minutes later, the examiner asks the patient to do the same thing again. If the patient points to the same part of the body both times and the area is within a centimeter of the posterior superior iliac spine, then it’s considered to be a positive test result.
SI Joint Dysfunction Self-Test
In addition to the other physical tests listed above, there are a few simple tests you may be able to perform on your own to help determine the source of your lower back pain.
First, you can place your hands on either side of your lower back, with your thumbs on the two small “dimples” in your back above your tailbone. Apply pressure to the “dimple” on the side where you’re experiencing pain. If this reproduces your lower back pain, then you may have a sacroiliac joint issue.
Next, you can try standing on one leg, using the leg on the side where you’re normally experiencing pain. If standing on one leg recreates that pain you’ve been experiencing, then you may have SI joint dysfunction.
Lastly, you can try sitting with your leg on your affected side crossed over your other leg, with your ankle to your knee. If you experience pain in your lower spine when sitting like this, then you may have SI joint dysfunction.
If one or more of these tests reproduce your lower back/pelvic bone pain, contact a local spinal specialist like Dr. Courtney at Advanced Spine Center in Plano, TX. He can perform a physical exam and definitively diagnose you with SI joint dysfunction.
Diagnostic Imaging Tests
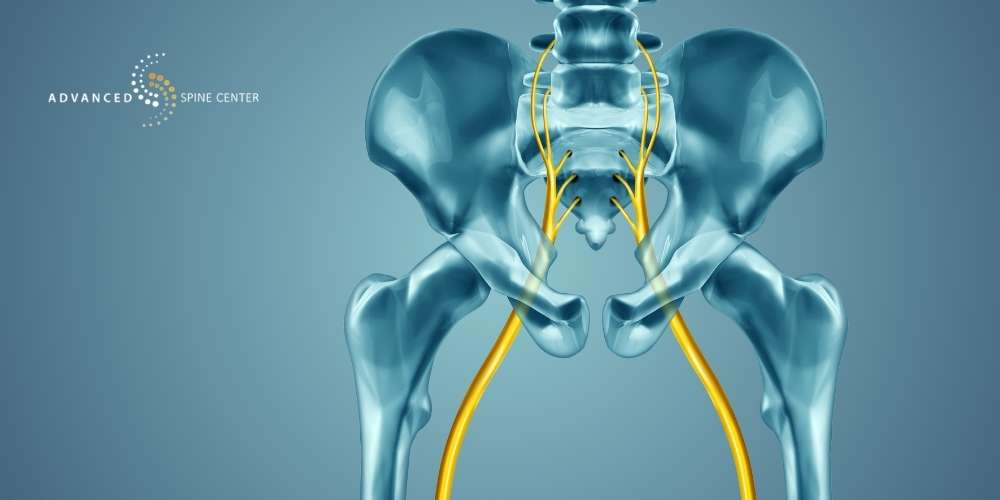
After performing a physical exam, an orthopedic specialist may also perform a diagnostic imaging test to confirm their diagnosis. Diagnostic imaging tests commonly used to diagnose SI dysfunction include X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) scans.
X-rays can reveal abnormalities such as fractures, arthritis, or misalignment of the SI joint. MRI scans provide detailed images of soft tissues, helping to identify inflammation, ligamentous injuries, or other structural abnormalities. CT scans offer cross-sectional images that can detect bony abnormalities or fractures with high precision.
Achieve SI Joint Pain Relief in Plano at the Advanced Spine Center
If you are suffering from chronic lower back pain and you suspect it’s the result of sacroiliac joint dysfunction, contact the Advanced Spine Center in Plano, TX. We provide our patients with thorough diagnostic testing to ensure an accurate diagnosis, and provide personalized treatment plans tailored to meet each patient’s unique needs and goals.
Sacroiliac joint pain can cause limited mobility and can result in widespread pain across the lower back and into the groin, buttocks, hips, and pelvis. Don’t let SI joint pain hold you back any longer–schedule an appointment with Dr. Courtney at Advanced Spine Center. We can provide you with a variety of treatment options for sacroiliac joint pain, including sacroiliac joint injection therapy, physical therapy, or even various surgical interventions.
Call (972) 499-5457 or contact us online to schedule an appointment and take your first step toward a pain-free you.










